-
Zomatos marketing strategy
Zomatos marketing strategy uses digital marketing channels like search ads,third party ads,SEO strategies,social media marketing and other types of strategies.
Zomato uses a very best and attention seeking strategy by using social media such as memes which are very humorous and attractive memes are very much trending and people’s are making memes for entertainment purposes and zomato is making its own sets of memes about food and grabbing attention of the people’s.



These are some of the memes and trending content on social media which is used by zomato for the purpose of marketing.these types of content are very much attractive and people’s are more on to it. these type of strategies are unique and trending which makes zomato to stand out from its competitors.
However, the key lesson to learn from Zomato’s promotion strategy is not just how it creates unique and trending content, but also the way it distributes it. Content distribution is as important as creating personalized and interesting content, and many brands seldom fail to identify this. Zomato’s content marketing strategy involves not just creating fresh content, but also reusing it across various distribution platforms, and tweaking it to ensure it is apt for each channel. From social media and email marketing to text messages, its content taps into the audience’s needs and interests, without being too pushy.
1.Customer centricity relevance content
Zomato understands what kind of content works for each platform.an example of zomato’s customer centric approach was seen during the beginning of the Covid pandemic in India.When the nationwide lockdown was enforced, Zomato understood the plight of its customers and quickly expanded to not just food but even groceries. It had introduced Zomato Market, a feature in the app that enabled grocery deliveries across the country. In addition, it was quick to announce contactless payment and delivery options to customers, which were instantly added to the app. While this is not directly a part of Zomato’s marketing strategy, the way its features are showcased to customers even on its app makes a whole lot of difference. In the long run, this focus may translate to customer loyalty and even brand recognition.
2.Notifications based on mood
Nowadays, apps use notifications and timely messages to grab attention, but if the message is too pushy, customers are more likely to ignore it or even go a step further to block it. Zomato ensures that even its notifications are interesting and something the customer will look forward to. Its cheeky humor was even noticed by superstar Hritik Roshan, who shared the below-mentioned screenshot. Not only does it add humor, but it also delivers the message in a way that is subtle yet interesting.
3.Social media memes
On social media, Zomato is a name to reckon with, not only for its services, but the incredible content it creates to interact with its large customer base. The brand not only posts memes relating to external topics, but it has the ability to make fun of itself too. Take its Twitter profile for example, which is full of hilarious content, all of which ultimately focuses on the brand’s offerings. Zomato understands that food cravings are real. In keeping with that, it publishes content that is amusing, yet focused on reminding the audience to order food from them.
These are some of the unique and standout strategies used by zomato.
-
What is market research
Market research, also known as “marketing research,” is the process of determining the viability of a new service or product through research conducted directly with potential customers.
ions and make informed decisions.
Market research can be conducted directly by organizations or companies or can be outsourced to agencies that have expertise in this process.
The process of market research can be done through deploying surveys, interacting with a group of people also known as a sample, conducting interviews, and other similar processes.
Market research can be conducted directly by organizations or companies or can be outsourced to agencies that have expertise in this process.
The process of market research can be done through deploying surveys, interacting with a group of people also known as a sample, conducting interviews, and other similar processes.
The primary purpose of conducting market research is to understand or examine the market associated with a particular product or service, to decide how the audience will react to a product or service. The information obtained from conducting market research can be used to tailor marketing/ advertising activities or to determine what are the feature priorities/service requirement (if any) of consumers.
Three key objectives of market research
A market research project may usually have 3 different types of objectives.
- Administrative: Help a company or business development, through proper planning, organization, and both human and material resources control, and thus satisfy all specific needs within the market, at the right time.
- Social: Satisfy customers’ specific needs through a required product or service. The product or service should comply with a customer’s requirements and preferences when consumed.
- Economical: Determine the economical degree of success or failure a company can have while being new to the market, or otherwise introducing new products or services, thus providing certainty to all actions to be implemented.
Why is market research important?
Conducting research is one of the best ways of achieving customer satisfaction, reducing customer churn and elevating business. Here are the reasons why market research is important and should be considered in any business:
- Valuable information: It provides information and opportunities about the value of existing and new products, thus, helping businesses plan and strategize accordingly.
- Customer-centric: It helps to determine what the customers need and want. Marketing is customer-centric and understanding the customers and their needs will help businesses design products or services that best suit them. Remember that tracing your customer journey is a great way to gain valuable insights into your customers’ sentiments toward your brand.
- Forecasts: By understanding the needs of customers, businesses can also forecast their production and sales. Market research also helps in determining optimum inventory stock.
- Competitive advantage: To stay ahead of competitors market research is a vital tool to carry out comparative studies. Businesses can devise business strategies that can help them stay ahead of their competitors.
Types of Market Research: Market Research Methods and Examples
Whether an organization or business wishes to know the purchase behavior of consumers or the likelihood of consumers paying a certain cost for a product, market research helps in drawing meaningful conclusions.
Depending on the methods and tools required, the following are the types:
1. Primary Market Research (A combination of both Qualitative and Quantitative Research):
Primary market research is a process where organizations or businesses get in touch with the end consumers or employ a third party to carry out relevant studies to collect data. The data collected can be qualitative data (non-numerical data) or quantitative data (numerical or statistical data).
While conducting primary market research, one can gather two types of information: Exploratory and Specific. Exploratory research is open-ended, where a problem is explored by asking open ended questions in a detailed interview format usually with a small group of people, also known as a sample. Here the sample size is restricted to 6-10 members. Specific research, on the other hand, is more pinpointed and is used to solve the problems that are identified by exploratory research.
- Focus groups:
Focus group is one of the commonly used qualitative research methods. Focus group is a small group of people (6-10) who typically respond to online surveys sent to them. The best part about focus group is the information can be collected remotely, can be done without personally interacting with the group members. However, this is a more expensive method as it is used to collect complex information.
- One-to-one interview:
As the name suggests this method involves personal interaction in the form of an interview, where the researcher asks a series of questions to collect information or data from the respondents. The questions are mostly open ended questions and asked in a way to facilitate responses. This method is heavily dependent on the ability and experience of the interviewer to ask questions that evoke responses.
- Ethnographic research:
This type of in-depth research is conducted in the natural settings of the respondents. This method requires the interviewer to adapt himself/herself to the natural environment of the respondents which could be a city or a remote village. Geographical constraints can be a hindering factor in conducting this kind of research. Ethnographic research can last from a few days to a few years.
2. Secondary Market Research:
Secondary research uses information that is organized by outside sources like government agencies, media, chambers of commerce etc. This information is published in newspapers, magazines, books, company websites, free government and nongovernment agencies and so on. The secondary source makes use of the following:
- Public sources: Public sources like library are an awesome way of gathering free information. Government libraries usually offer services free of cost and a researcher can document available information.
- Commercial sources: Commercial source although reliable are expensive. Local newspapers, magazines, journal, television media are great commercial sources to collect information.
- Educational Institutions: Although not a very popular source of collecting information, most universities and educational institutions are a rich source of information as many research projects are carried out there than any business sector.
Why Does Every Business Need Market Research?
Market research is one of the most effective ways to gain insight into your customer base, competitors, and the overall market. The goal of conducting market research is to equip your company with the information you need to make informed decisions.
It is especially important when small businesses are trying to determine whether a new business idea is viable, looking to move into a new market, or are launching a new product or service. Read below for a more in-depth look at how market research can help small businesses.
- COMPETITION According to a study conducted by Business Insider, 72% of small businesses focus on increasing revenue. Conducting research helps businesses gain insight into competitor behavior. By learning about your competitor’s strengths and weaknesses, you can learn how to position your product or offering. In order to be successful, small businesses need to have an understanding of what products and services competitors are offering, and their price point.
- CUSTOMERS Many small businesses feel they understand their customers, only to conduct market research and learn they had the wrong assumptions. By researching, you can create a profile of your average customer and gain insight into their buying habits, how much they’re willing to spend, and which features resonate with them. Additionally, and perhaps more importantly, you can learn what will make someone use your product or service over a competitor.
Learn more: Customer Satisfaction Survey
- OPPORTUNITIES Potential opportunities, whether they are products or services, can be identified by conducting market research. By learning more about your customers, you can gather insights into complementary products and services. Consumer needs change over time, influenced by new technology and different conditions, and you may find new needs that are not being met, which can create new opportunities for your business.
FORECAST A small business is affected by the performance of the local and national economy, as are its’ customers. If consumers are worried, then they will be more restrained when spending money, which affects the business. By conducting research with consumers, businesses can get an idea of whether they are optimistic or apprehensive about the direction of the economy, and make adjustments as necessary. For example, a small business owner may decide to postpone a new product launch if it appears the economic environment is turning negative.
Marketing Research vs. Market Research
Market research and marketing research are frequently used interchangeably; in some cases, they are, particularly for those outside the sector. However, the two names are not interchangeable in the business.
Because they are similar, the names are frequently used interchangeably. They are both fundamental parts of marketing, which implies they occur before selling the product or service.
Marketing research entails investigating new goods, distribution channels, and product development. Depending on the setting, it can also involve promotion research, pricing, advertising, and public relations. It has a considerably broader reach and may thus be utilized to determine a marketing plan.
Marketing Research is also far more technical, systematic, scientific, and objective than Market research.
Differences Between Market Research and Marketing Research
We understand that these terms might be used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings.
Let’s go straight into the differences between market research and marketing research. The distinction between market research and marketing research is easily discernible on the following grounds:
- Market research is the study of customers and the market, whereas marketing research is the study of all aspects of marketing.
- Market research is reliant, whereas marketing research is autonomous.
- Marketing research has a much broader reach since it involves doing product research and customer preferences, whereas market research just involves gathering market information.
- Market research investigates the market success of a product or service, whereas marketing research collects data for marketing intelligence activities and decision-making.
- Market research is focused on answering particular questions, whereas marketing research is more general and utilized to solve various marketing challenges.
-
How has internet changed indian economy
The Internet economy contributed up to $537.4 billion to India’s GDP in 2020, of which a minimum of $270.9 billion was contributed by apps. Apps were contributing 70% to the mobile traffic. A World Bank study finds that every 10% increase in broadband penetration boosts GDP growth by 1.38 % in developing countries.
Technological advancement helps to optimize supply of goods and services qualitatively and quantitively, which is essential for prosperity. The market sure has grown since digitization and technical advancements started to influence the production, which in turn impacted supply of commodities and services.
India moved toward a market economy and expanded in areas like information technology. What social reforms has the Indian government made over the last few decades? Women and dalits have gained more rights to education and employment.
Technology can save the time it takes to produce a good or deliver a service, contributing to the overall profits of a business. Technology can contribute to the efficiency of a business’s output rate, allowing for larger quantities of products to be moved or of services to be rendered.
2)How has internet transformed indian rural economy
The number of internet users in rural India increased 18 percent last year, faster than growth in urban areas and continuing a trend that started two years ago.
Internet users in urban India increased 5 percent in 2021. Rural India has 351 million users, or 37 percent of people there, according to a report by the Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI) and data analytics company KANTAR. Around 762 million Indians have not adopted the internet yet–out of which 63 per cent live in rural areas.
‘Difficulty to understand the Internet’, is the primary deterrent along with lack of awareness, especially in rural India. Goa has the maximum internet penetration and Bihar the lowest among states, the report said.
The number of internet users will grow by over 200 million in the next two years and there will be 900 million of them by 2025, the report said. Internet growth in urban India seems to have hit a plateau, with 341 million users and 69 per cent penetration.
The report titled ‘Internet in India’ is based on a survey of 77,000 households across all states and Union Territories, excluding Lakshadweep.
As many as 346 million Indians are engaged in online transactions such as e-commerce and digital payments: that is more than the US population. Indian transactions jumped significantly during the coronavirus pandemic, as the report noted a record 51 per cent increase from 230 million transactions in 2019.
Innovation in India’s Rural Economy
Disruptive business models are stimulating inclusive growth in agriculture and rural finance
- Sectors that comprise India’s rural economy contribute to nearly half of the nation’s GDP and is growing steadily, supported by government and private sector improvements to the physical and digital infrastructure.
- The agricultural economy is on the cusp of massive disruption. Companies that address inefficiencies across the value chain will have explosive growth potential. As new generations of farmers take the reins, technology will play a greater role in the agriculture value chain.
- The sector also needs faster and better access to financing. Innovative business model and technology adoption is driving access to microfinance, agri, and consumer loans.
3)how does social media encouraged entrepreneurship
In addition to the fact that social media offers a platform where it allows business and entrepreneurs to communicate rapidly and economically with clients as well as it also allows them to build a database that can be used to generate business leads that may translate to enhanced the sales and results growth of the business.
Social media networks help you increase your contacts. Using the correct platform you can spread knowledge about your products and services. If needed you can also find investors and people who are interested to invest in your ideas and business. There can be no other better way than Social media to attract customers.
1. Find Areas Of Interest To Get Them Involved
Finding areas that resonate with young people can help them get involved, especially if it is something that involves peers, where they could see themselves in that position, and then develop a sense of fellow feeling about helping them. Also, planning some places where young people can get actively involved helps, so they see others in those roles and understand that they can do the same kinds of things. – Gloria Horsley, O
2. Help Them Embrace Their Passion For Social Good
The great thing about millennials is that they’re not only quite entrepreneurial, but they’re also socially responsible and interested in giving back. Helping them embrace their passion around social good — through things like education, mentorship, tech resources and pro bono services — will allow them to take the entrepreneurial leap and put their ideas into action! – Jeff Rosset, The Chicago Leadership Alliance
Forbes Nonprofit Council is an invitation-only organization for chief executives in successful nonprofit organizations.
3. Teaching Empathy Is Key
Teaching young people more about empathy is key to encouraging them to take more engaged social action, and deliver appropriate entrepreneurial solutions to social problems. By putting yourself in the shoes of your beneficiaries and learning how to become more empathetic, youths will develop more passion for their work and produce realistic solutions that listen to, and serve, their beneficiaries.
4. Youths Are Seeking Meaningful Opportunities
Young people are searching for meaningful opportunities in social entrepreneurship. The more responsibility, ownership, and impact involved in the role, the better. – For example, ENVenture is a social enterprise in Uganda that pairs recent graduates as Business Development Fellows that are in charge of setting up a clean energy business in a rural village with a host organization.
5. Show Others Pursuing Social Entrepreneurship
Seeing other young people successfully pursuing social entrepreneurship is the most important thing we can do to encourage more young people to pursue the space. Social entrepreneurship programs and awards, on-campus programs, online videos and podcasts are all helping young people realize that social entrepreneurship can be a meaningful and impactful career choice.
-
Reasons for Nokia’s failure
The reasons why Nokia failed after enjoying unrivalled dominance in the mobile segment for several years. The ferocious and mighty telecom giant Nokia was well known for its products’ hardware and battery life.
For years, it was the talk of the town. User satisfaction with Nokia’s mobiles was globally recognized. The company launched the first internet-enabled phone in 1996 and by the start of the millennium, Nokia also released a touch-screen mobile prototype.
This was the start of a revolution in the mobile phone industry. The Finnish giant was the largest cell phone maker in 1998. Nokia overtook Motorola, a move that was hard to predict. So what led to the downfall of Nokia? It wasn’t a single factor but a myriad of reasons, most of which resulted from Nokia’s resistance to change. We present to you the 6 main reasons behind Nokia’s failure.
Reasons for Nokia Failure
- The Resistance To Smartphone Evolution
- The Deal With Microsoft
- Nokia’s Failed Marketing Strategies
- Moving Too Slow With The Industry
- Overestimation Of Strength
- Lack Of Innovation In Products
The Resistance To Smartphone Evolution
Nokia failed to take advantage of the Android bandwagon. When mobile phone manufacturers were busy improving and working on their smartphones, Nokia remained stubborn. Samsung soon launched its Android-based range of phones that were cost-effective and user-friendly.
Nokia’s management was under the impression that people wouldn’t accept touch screen phones and would continue with the QWERTY keypad layout. This misapprehension was the start of its downfall. Nokia never considered Android as an advancement and neither wanted to adopt the Android operating system.
After realizing the market trends, Nokia introduced its Symbian operating system. However, it was too late by then with Apple and Samsung having cemented their positions. It was difficult for the Symbian operating system to make any inroads. This is the biggest reason behind Nokia’s downfall.
The Deal With Microsoft
Another reason for Nokia’s failure was the ill-timed deal with the tech giant, Microsoft. The company sold itself to Microsoft at a time when the software behemoth was fraught with losses.
Nokia’s sales screamed the mobile phone maker’s inability to survive on its own. At the same time, Apple and Samsung were making significant strides in innovation and technological developments.
It was too late for Nokia to adapt to the dynamic and rigorous changes in the market. Microsoft’s acquisition of Nokia is considered to be one of the biggest blunders and wasn’t fruitful for either side.
Nokia’s Failed Marketing Strategies
Generally, a startup fails because of a bad marketing strategy, and the same happened with Nokia. The company followed an unsuccessful strategy of umbrella branding. Apple was the first company to apply the umbrella branding model with the iPhone at the top. It kept adding new models to this umbrella year after year. Samsung followed the same route by launching the Samsung Galaxy series but Nokia failed to take cues.
The user trust Nokia built over the years was gradually waning. The company was inefficient in its selling and distribution methods. Seeing the mess, Nokia decided to come up with some fascinating hardware and software innovations. However, these were already released by Nokia’s rivals and lacked uniqueness. Failure in Nokia’s marketing and distribution strategies played a significant role in its elimination from the mobile industry market.
Moving Too Slow With The Industry
Nokia never kept pace with changing technology and trends. Nokia was always famous for its hardware and didn’t pay much attention to its software line-up. Initially, the company overlooked technical advancements to avoid the risks associated with bringing innovation to phones.
The business needed diversion but it was too late by the time Nokia realized this. Instead of being amongst the early initiators, Nokia transitioned when almost every major brand had already started producing awesome phones.
Overestimation Of Strength
Nokia overestimated its brand value. The company believed that even after the late launch of its smartphones, people would still flock to stores and purchase Nokia-manufactured phones. A misconception! People still make predictions of Nokia retaining the market leadership if it uses better software at its core. However, this is far from the truth as seen today.
The company got stuck with its software system which is known to have several bugs and clunks. Nokia felt its previous glory would help alleviate any sort of trouble. Unfortunately, things didn’t play out that way.
Lack Of Innovation In Products
The lack of innovation in its products only added to Nokia’s woes. While brands like Samsung and Apple came up with advanced phones every year, Nokia simply launched the Windows phone with basic features.
The Nokia Lumia series was a jump-start measure, but even that collapsed due to a lack of innovation. The unattractive and dull features didn’t help. In the era of 4G, Nokia didn’t even have 3G-enabled phones. Nokia also came up with the Asha series but it was game over by then.
Wrong decisions and risk aversion brought the decline of the mobile giant. Nokia refrained from adopting the latest tech. Nokia’s failure became a case study that made organizations realize the importance of continuous evolution and enhancements. The journey of what was once the world’s best mobile phone company to losing it all by 2013 is quite tragic. Nokia also strongly lacked leadership and guidance.
Bounce back of Nokia

How Nokia Bounced Back (With the Help of the Board)
To help the former mobile giant find a radically new strategic direction, Nokia’s board assumed a unique role.
Nokia’s mobile-phone downfall – from a 40 percent market share to near bankruptcy in just a few years – has become a familiar cautionary parable on the perils of industry disruption. Less well-known is the equally instructive tale of how Nokia clawed its way back from the edge of destruction. Indeed, since touching bottom in 2012, its market capitalisation, while not at the level of its pre-smartphone heyday, has increased more than five-fold.
Nokia’s recovery was due to a wholesale strategic shift towards telecommunications networks, culminating in the US$16.6 billion acquisition of Alcatel-Lucent, a deal completed in 2016. Rarely has any large company reinvented itself so quickly and radically. But before the strategic redirection could be accomplished, the company needed to repair deep-seated cultural problems. Nokia’s revamped board of directors (a new chairman was appointed in 2012) proved integral to this effort. The emotion-regulating processes used by Nokia’s board to counter internal dysfunction are the subject of our recent article, which won the 2018 Best Paper Award of the Academy of Management’s Strategizing Activities and Practices Interest Group.
A culture of fear
From 2012-2017, we conducted in-depth interviews with 120 Nokia personnel, ranging in rank from upper-middle managers to board members and C-suite leaders.
Interviewees who experienced Nokia’s decline first-hand described to us how negative emotional dynamics at the very top harmed communication and strategic decision making. An authoritarian culture of fear pervaded multiple levels of management, producing a shoot-the-messenger mentality and rampant defensiveness. Fearing for their jobs, managers stayed quiet when top leaders latched onto losing strategic options – such as sticking with the Symbian operating system despite serious technical issues. The company remained paralysed as plummeting performance led to the CEO’s exit in 2010.
With the new CEO installed, Nokia had to choose an external operating system to replace Symbian. Windows and Android were the front-runners. Two emotional obstacles contributed to the ill-fated decision in favour of Windows (contrary to the advice of McKinsey consultants). First was the fear factor: Since the CEO had previously worked at Microsoft, some managers assumed the only mind that mattered had already been made up, and dissenters would be targeted for termination. Second, top managers were able to avoid coping with the enormity of the decision by framing it internally as a temporary measure to stop the bleeding. Of course, the haemorrhage only worsened after the alliance with Microsoft was announced; market capitalisation declined by 50 percent between January 2011 and January 2012.
Good strategy starts with emotional safety
In 2012, Nokia replaced its chairman along with three board directors. Right from the start, the chairman focused on radically improving the emotional relationship between the board and management. He recognised that Nokia’s strategic stasis was linked to a lack of openness. “If the board is a place where the management comes with knees trembling, a single solution in their mind, that they need to sell to the board, there is no way for the board to contribute,” he told us.
The board coaxed hyper-cautious and self-protective managers out of their shells with principles such as “No news is bad news, bad news is good news, and good news is no news.” Consequently, conversations between directors and managers took on newfound candor and depth.
Disengaging from past strategy
The new board also perceived that managers’ emotional attachment to the existing Windows strategy – about which warning signs were already flashing – could prevent them from considering other options. Rather than thoroughly re-evaluating the situation and creating new options, they were at risk of behaving defensively and avoiding the whole issue.
Directors, then, sought to dispel the dread by explicitly raising the prospect of failure in open conversations. They also pre-empted managers’ defensiveness by establishing agreed-upon courses of action should the Windows Phone continue to underperform. By pegging future actions to objective performance data rather than making them subject to later discussion, directors reduced the biasing role of emotions in planning the next strategic steps.
This approach also forced managers to begin making contingency plans. Directors insisted on seeing a range of prospective scenarios according to a systematic process. The board’s guidance helped managers balance out their appraisal of the various options and achieve a more nuanced emotional standpoint. As a result, they were able not only to conceive of radically new strategic possibilities but also to anticipate outcomes – both good and bad.
The idea of exiting the mobile phone business presented itself when leaders realised that a continuation of Nokia’s current strategy would require large additional investments from its partner Microsoft. But what value could Microsoft possibly derive from rescuing Nokia? It became clearer and clearer that the Windows strategy was untenable. A more likely scenario was that Microsoft would offer to buy Nokia’s mobile phone division – which would lead Nokia into truly uncharted territory. Here again the board’s efforts to root out emotional investment in the status quo enabled managers to envision a post-phone future for the firm. The deal with Microsoft was pursued and, in September 2013, completed for US$7.2 billion.
Concurrently, Nokia jumped into networks with both feet by buying back the joint venture Nokia Siemens Networks (NSN). The purchase of NSN was made possible by a hefty financing package that was negotiated as part of the larger Microsoft-Nokia deal. “So in a funny way, we got Microsoft to fund the new Nokia and help [rebuild] it”, the chairman told us.
Even though the divestment of the phone business shattered Nokia’s old identity, top managers’ emotions transformed during the strategy formulation process and eventually supported the new strategy. Out of the tumultuous anxiety of competing perspectives arose a shared enthusiasm for the course the company had chosen. A top manager credits his own embrace of the strategic direction to the “crazy amount of groundwork”, i.e. the extensive scenario analyses and number-crunching, necessitated by deep and frequent dialogues with the board.
We all are Nokia
Nokia’s comeback story is unique: Where else have we seen an iconic company fail utterly at what it’s famous for, then promptly pivot to find success in a vastly different area? This was not a turnaround akin to IBM’s, where the company learnt to leverage existing core strengths (i.e. mainframes) in a new way.
But in our fast-changing world, we may be seeing more and more cases like Nokia’s. As disruption accelerates, companies will increasingly have to reckon with the unravelling of entire business models, if not entire industries. Rather than defensively clinging to the mast of their sinking ship, managers will need to take to the lifeboats and never look back.
But it isn’t easy to be stoic when you’ve worked tirelessly for years to make the obsolete strategy work. Inevitably, managers will feel emotionally invested in the status quo, with their egos bound up in the company’s past successes. Confronting the reality of radical strategic change raises fears and vulnerabilities that few of us are comfortable with, least of all the high-flying overachievers in the C-suite.
Day-to-day business in most organisations offers scant opportunity for senior managers to work out their negative emotions about radical change. According to the mainstream professional mindset, emotions have no place at work. So managers learn to cloak their emotional biases in supposedly “rational” objections. They often convince themselves that these rationalisations constitute sound arguments and will staunchly defend them. Under such conditions, it is almost impossible to devise a thoughtful and creative strategy for dealing with radical change.
The board, therefore, is uniquely positioned to perform interventions designed to regulate top managers’ emotions, thus ensuring the quality and integrity of the strategy-formulation process. Why the board? Directors ideally reside above the fray, only provisionally committing to a particular strategic direction. Relative to outsiders such as management consultants, directors are also more context-savvy and share with top managers the common goal of seeing the firm succeed in the long term. While the mandate of the board does not traditionally encompass emotional regulation, such a role is well within the board’s central duty to oversee organisational strategy.
-
Information about brand
The term brand refers to a business and marketing concept that helps people identify a particular company, product, or individual. Brands are intangible, which means you can’t actually touch or see them. As such, they help shape people’s perceptions of companies, their products, or individuals. Brands commonly use identifying markers to help create brand identities within the marketplace. They provide enormous value to the company or individual, giving them a competitive edge over others in the same industry. As such, many entities seek legal protection for their brands by obtaining trademarks.
- A brand is an intangible marketing or business concept that helps people identify a company, product, or individual.
- People often confuse brands with things like logos, slogans, or other recognizable marks, which are marketing tools that help promote goods and services.
- Brands are considered to be among a company’s most important and valuable assets.
- Companies can protect their brands by registering trademarks.
- Types of brands include corporate, personal, product, and service brands.
Understanding Brands
As mentioned above, a brand is an intangible asset that helps people identify a specific company and its products. This is especially true when companies need to set themselves apart from others who provide similar products on the market, including generic brands. Advil is a common brand of ibuprofen, which the company uses to distinguish itself from generic forms of the drug available in drugstores. This is referred to as brand equity.
People often confuse logos, slogans, or other recognizable marks owned by companies with their brands. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are distinct. The former are marketing tools that companies often use to promote and market their products and services. When used together, these tools create a brand identity. Successful marketing can help keep a company’s brand front and center in people’s minds. This can spell the difference between someone choosing your brand over your competitor’s.
brand is considered to be one of the most valuable and important assets for a company. In fact, many companies are often referred to by their brand, which means they are often inseparable, becoming one and the same. Coca-Cola is a great example, where the popular soft drink became synonymous with the company itself. This means it carries a tremendous monetary value, affecting both the bottom line and, for public companies, shareholder value
History of Brands
Brands have long been used to set products apart over the course of history. The idea of branding may go as far back as 2000 B.C., where merchants used it to sell their wares in different markets. At that time, it was commonly used as a technique to denote ownership of a product or a piece of property.2
Branding has been used throughout the ages. In the 13th century, Italians began putting watermarks on their paper as a form of branding. The term brand also refers to the unique marks burned into the hides of cattle to distinguish the animals of one owner from those of another.3
But one of the most popular uses was in rural America. You’ve probably heard of the term branding, which was used by cattle ranchers, who used to brand their livestock as a form of identification. Brands started taking off after companies started packaging their goods in the 19th century to distinguish themselves from other companies.
Online brand
Internet branding (also referred to as Online branding) is a brand management technique that uses the World Wide Web & Social Media Channels as a medium for positioning a brand in the marketplace.[1] Branding is increasingly important with the advancements of the internet. Most businesses are exploring various online channels, which include search engine, social media, online press releases, online marketplace, to establish strong relationships with consumers and to build their brands awareness.
Disadvantages of brand
1. Discourages from Trying other Products
Brand loyalty discourages the consumer from trying out other new brands which possibly be more satisfying.
2. Leads to Monopoly
3. Create Confusion
4. Commands Premium
5. Substandard Goods
6. Imposes Responsibility
7. Some Products Do Not Lend Themselves to Branding
8. Switch to Another Product
9. Expensive
Building up brand recognization and loyalty is very expensive. Particularly, small sized companies cannot afford it.
10. Increase Cost
Branding needs heavy and widespread Advertising, attractive packaging and effective sales and widespread Advertising, attractive packaging, and effective sales promotion.
Characteristics of a Successful Brand
1. Competitiveness
For a brand to truly succeed it needs to be as competitive as possible. This includes having an entire team working behind a brand, from the most basic administrative assistants to those in a higher power position. There is no use in sitting back and hoping for the best; a successful brand goes above and beyond consumer expectations to remain on the cutting edge of its industry.
2. Distinctiveness
To have a memorable brand identity you need to be distinctive. Some of the world’s most popular brands, such as Apple, Starbucks and Domino’s Pizza, have successfully achieved this. For instance, Apple is widely known for its minimalist approach to design and technology as well as its innovative products. Starbucks is known for its high-quality goods and services that are consistent across every store worldwide. Giving your customers a specific reason to use your services will without doubt keep them returning to your brand, time and time again.
3. Passion
Though it’s possible to build a brand on a short-term basis without passion, maintaining the success of that brand over the long term is incredibly difficult without passion. Some of the world’s most successful people, such as Steve Jobs, Roger Federer and Oprah Winfrey, did not or have not succeeded without passion.
Passion is the force that drives us even through the most challenging of moments, propelling us to work harder than everyone else to continually deliver greatness. If you possess a genuine passion for your brand, that passion will rub off on your customers who will feel just as enthusiastic and excited about your products or services as you are.
4. Consistency
With all of the above being said, it is still important to be consistent in everything you do as a brand. Consistency is the blood that runs through your brand, differentiating it from the competition and enabling it to remain in the memories of your consumers for longer. It also brings familiarity to your brand, which automatically leads to loyalty. Provided you consistently deliver high-quality goods and services, you can expect your customers to return back to your business in future.
5. Leadership
The world’s greatest brands are supported by influential leaders who continually aspire for greatness. Whether that involves a sports team, a large corporation or a small business, the most successful of these will have an influential leader backing them. When you think of Apple you immediately think of Steve Jobs, who was an extraordinary leader who taught us all many valuable lessons about strength and leadership.
As a business owner, you need to live and breathe your brand in order to inspire both your workforce and your clientele to possess the same enthusiasm and passion for your brand. This in turn will lead everyone associated with your brand to feel deeply affiliated with it as your passion for what you do truly shines through.
6. Exposure
Another important characteristic of a successful brand is exposure. Well-known sports brand, Puma, combines numerous marketing channels to reach out to its target audience, including video, social media and experiential marketing to truly immerse its customers into the brand.
Although you may not have a budget as vast as Puma’s, thanks to the internet it has never been easier to increase exposure of your business. By developing a presence on social media sites such as Instagram, Facebook and Twitter and reaching out to customers through multiple channels, you have a better chance than ever to reach consumers and establish your brand on a global scale.
Top 7 Characteristics of a Successful Brand
1. Competitiveness
For a brand to truly succeed it needs to be as competitive as possible. This includes having an entire team working behind a brand, from the most basic administrative assistants to those in a higher power position. There is no use in sitting back and hoping for the best; a successful brand goes above and beyond consumer expectations to remain on the cutting edge of its industry.
2. Distinctiveness
To have a memorable brand identity you need to be distinctive. Some of the world’s most popular brands, such as Apple, Starbucks and Domino’s Pizza, have successfully achieved this. For instance, Apple is widely known for its minimalist approach to design and technology as well as its innovative products. Starbucks is known for its high-quality goods and services that are consistent across every store worldwide. Giving your customers a specific reason to use your services will without doubt keep them returning to your brand, time and time again.
3. Passion
Though it’s possible to build a brand on a short-term basis without passion, maintaining the success of that brand over the long term is incredibly difficult without passion. Some of the world’s most successful people, such as Steve Jobs, Roger Federer and Oprah Winfrey, did not or have not succeeded without passion.
Passion is the force that drives us even through the most challenging of moments, propelling us to work harder than everyone else to continually deliver greatness. If you possess a genuine passion for your brand, that passion will rub off on your customers who will feel just as enthusiastic and excited about your products or services as you are.
4. Consistency
With all of the above being said, it is still important to be consistent in everything you do as a brand. Consistency is the blood that runs through your brand, differentiating it from the competition and enabling it to remain in the memories of your consumers for longer. It also brings familiarity to your brand, which automatically leads to loyalty. Provided you consistently deliver high-quality goods and services, you can expect your customers to return back to your business in future.
5. Leadership
The world’s greatest brands are supported by influential leaders who continually aspire for greatness. Whether that involves a sports team, a large corporation or a small business, the most successful of these will have an influential leader backing them. When you think of Apple you immediately think of Steve Jobs, who was an extraordinary leader who taught us all many valuable lessons about strength and leadership.
As a business owner, you need to live and breathe your brand in order to inspire both your workforce and your clientele to possess the same enthusiasm and passion for your brand. This in turn will lead everyone associated with your brand to feel deeply affiliated with it as your passion for what you do truly shines through.
6. Exposure
Another important characteristic of a successful brand is exposure. Well-known sports brand, Puma, combines numerous marketing channels to reach out to its target audience, including video, social media and experiential marketing to truly immerse its customers into the brand.
Although you may not have a budget as vast as Puma’s, thanks to the internet it has never been easier to increase exposure of your business. By developing a presence on social media sites such as Instagram, Facebook and Twitter and reaching out to customers through multiple channels, you have a better chance than ever to reach consumers and establish your brand on a global scale.
7. Audience knowledge
Last but not least, you cannot achieve any of the above without having a thorough knowledge of your target audience. You can easily do this by performing in-depth research about the demographics of your target audience.
This not only improves the quality of your content but also helps you to communicate with your audience in a way that directly appeals to them, which in turn encourages you to create a strong, human connection between your business and your target audience.
-
Hyundai motors case study
Hyundai Motor Company, a major company in the Hyundai Kia Automotive Group which is the world’s fifth largest automaker as of the end of 2009, (In 2008, Hyundai ranked the eighth largest auto maker, without including Kia.) and the world’s fastest growing automaker.
Headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, Hyundai operates the world’s largest integrated automobile manufacturing facility in Ulsan, which is capable of producing 1.6 million units annually. The company employs about 75,000 persons around the world, Hyundai vehicles are sold in 193 countries through some 6,000 dealerships and showrooms worldwide.
The Hyundai logo, a slanted, stylized ‘H’, symbolizes the company shaking hands with its customer. Hyundai translates from the word “modernity”, and is pronounced as “Hyon-dae” in Korean.
Chung Ju-Yung founded the Hyundai Engineering and Construction Company in 1947. Hyundai Motor Company was later established in 1967. The company’s first model, the Cortina, was released in cooperation with Ford Motor Company in 1968. When Hyundai wanted to develop their own car, they hired George Turnbull, the former Managing Director of Austin Morris at British Leyland. He in turn hired five other top British car engineers. They were Kenneth Barnett body design, engineers John Simpson and Edward Chapman, John Crosthwaite as chassis engineer and Peter Slater as chief development engineer. In 1975, the Pony, the first Korean car, was released, with styling by Giorgio Giugiaro of Italian Design and power train technology provided by Japan’s Mitsubishi Motors. Exports began in the following year to Ecuador and soon thereafter to the Benelux countries. In 1991, the company succeeded in developing its first proprietary gasoline engine, the four-cylinder Alpha, and transmission, thus paving the way for technological independence.
In 1983, Hyundai exported the Pony to Canada, but not to the United States because the Pony didn’t pass emissions standards there. Canadian sales greatly exceeded expectations, and it was at one point the top-selling car on the Canadian market. The Pony afforded a much higher degree of quality and refinement in the lowest price auto segment than the Eastern-bloc imports of the period then available.
In 1986, Hyundai began to sell cars in the United States, and the Excel was nominated as “Best Product #10” by Fortune magazine, largely because of its affordability. The company began to produce models with its own technology in 1988, beginning with the midsize Sonata.
In 1998, Hyundai began to overhaul its image in an attempt to establish itself as a world-class brand. Chung Ju Yung transferred leadership of Hyundai Motor to his son, Chung Mong Koo, in 1999. Hyundai’s parent company, Hyundai Motor Group, invested heavily in the quality, design, manufacturing, and long-term research of its vehicles. It added a 10-year or 100,000-mile (160,000 km) warranty to cars sold in the United States and launched an aggressive marketing campaign.
In 2004, Hyundai was ranked second in “initial quality” in a survey/study by J.D. Power and Associates. Hyundai is now one of the top 100 most valuable brands worldwide. Since 2002, Hyundai has also been one of the worldwide official sponsors of the FIFA World Cup.
Hyundai has invested in manufacturing plants in the North America, China, Czech Republic, Pakistan, India, and Turkey as well as research and development centers in Europe, Asia, North America, and the Pacific Rim. In 2004, Hyundai Motor Company had $57.2 billion in sales in South Korea making it the country’s second largest corporation. Worldwide sales in 2005 reached 2,533,695 units, an 11 percent increase over the previous year. Hyundai has set as its 2006 target worldwide sales of 2.7 million units (excluding exports of CKD kits). In 2007 it reached 3,961,629 worldwide vehicle sales-surpassing Fiat, Chrysler, PSA/Peugeot, Nissan, and Honda.
Hyundai Motor Company’s brand power continues to rise as it was ranked 72nd in the 2007 Best Global Brands by Interbrand and BusinessWeek survey. Brand value estimated at $4.5 billion. Public perception of the Hyundai brand has been transformed as a result of dramatic improvements in the quality of Hyundai vehicles.
Hyundai is one of the leading groups of Companies founded in South Korea. It is the general trading house of Korea, which provides various import and export services. There are several types of products are included in its import and export services such as plants & machinery, automobiles, steel and chemical products, general commodities etc. Firstly it was founded as the construction company then the management of the company diversified its business activities in various business areas. The corporation operates its business worldwide through 34 worldwide offices. Through its global presence, it provides optimal solutions to the customer according their requirements. It is helpful to enhance its financial capability in the industry. Hyundai Motor Company is one of the divisions of the Hyundai Corporation, which is the fourth largest automaker in the world. Hyundai Heavy Industries division is the largest shipbuilder in the world (Hyundai Corporation, 2010).
Internal Environment Analysis
The analysis of the internal environment is an important component for the business as it helps to determine the effectiveness of the management strategies and the threats, which may cause problem for the organization. For the internal and external analysis the SWOT analysis tool could be used. The SWOT analysis tool would help to determine the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of an organization. The internal environment analysis of the Hyundai can be analyzed through the analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the organization –
Strenths:
Diversified business activities – The Company is involved in the diversified business segments as it provides several types of import and export services to its customer worldwide.
It is the largest automaker in Asia and fourth largest automaker in world, which enhance its effectiveness in global exposure. It also helps to capture a large amount of customer worldwide.
Information gathering capability -The information gathering capability of the company is effective as it obtains prompt and extensive information from its sources worldwide. It also uses the advanced trading techniques to obtain the extensive information.
Quality advantages – The quality of the Hyundai automobile is better than the other manufacturers in Asia as owners of Hyundai cars are experiencing less problems from the owners, who obtains other brand.
Sound financial position – The Hyundai Corporation is enjoying a continuous increase in its sales revenue worldwide, which is also causing an increase in the net income of the business (Hyundai Motor Company, 2010).
The business activities are operated in ethical and social manner, which causes an increase in the image of the company in the society.
Weaknesses:
An increase in the cost of production is reducing the net income of the company. It is also imposing commodity price risks on the company as the price of inputs such as steel, plastic, aluminum etc.
The company is also experiencing the exchange rate risk because of the worldwide business activities. The exchange rate risk is affecting the total revenue of the business. The fluctuation in the foreign exchange rates is affecting the business performance as it is involved in the import and export of several services.
Increase in debt to equity ratio – The Company is also experiencing an increase in the debt equity ratio, which exhibits an increase in the interest expenses of the company. The external financial obligation is also increasing, which may create financial problems for Hyundai (Hyundai Motor Company, 2010).
Analysis of the External Environment
The business of Hyundai also operates in the external environment and there are several opportunities and threats are produced by the external environment for the company. The analysis of the opportunities and threats helps to achieve the competitive position for the company. The analysis of the external factors is beneficial for the company if it is performed effectively and efficiently. Hyundai is one of the leading companies in the automobile industry and it has the following opportunities and threats –
Opportunities:
Entry in ship building business – It is the leading company in the heavy industry and entry in the ship building business would be effective for the business in order to enhance its revenue and market share as well.
New project development – The launching and development of the new projects and products would also cause an increase in the performance of the business in the industry. The increase in the demand for fuel efficient vehicles would also cause the success of the new launched projects and products.
Business expansion – Hyundai also have the opportunity of the business expansion as it is an Asian company and had the opportunity of expanding its business in Asian Pacific Market.
Reduction in cost – The Company operates its business in several countries around the globe and it can reduce its cost of production by enhancing the production capacity in the countries with lower amount of cost (Hyundai Motor Company, 2010).
Threats:
Environment regulations – The environment regulations are posing threats for the business as diversification of the business may cause the violation of the environmental regulations.
Declining economy – The decline in the economy is also causing a decrease in the market position of the company as well as also reducing the market capitalization of it.
Political problems – The business unit in the different countries may cause the problems for the business (Hyundai Motor Company, 2010).
Environmental Analysis
In the present contemporary environment every business operates its business activities in highly competitive environment. There are various environmental factors, which influences the operation of the organization.
Effect of Economic Environment
The Company is operating with a rapid economic growth in the business by capturing the environmental opportunities. The increase in the value of currency of Korea against the US dollar is also causing an increase in the profits of the business from the foreign business activities. Labor is not cheap in Korea but increase in the production capacity in the nations with lower wage rate is reducing overall cost of the business.
In 2009, Hyundai Motor Company succeeded in selling 2.4 million vehicles overseas, a meaningful accomplishment considering the global economic crisis. In particular, Elantra, Genesis, Genesis Coupe, Santa Fe, and Veracruz were recognized as the best and safest cars in their categories by leading agencies and the media in the US. Also, Hyundai achieved cumulative export sales of 1 million cars in Africa during the 33 years since it first began exporting to the region. Hyundai Motor Company pledges continuous growth by maximizing brand value in developed markets and expanding its sales capacity in emerging markets.
Effect of Industry Environment
Hyundai Motor Company was named Carmaker of the Year by AM, UK’s leading auto trade magazine, in the AM Awards 2010. Carmaker of the Year is awarded to companies that launch innovative vehicles that pioneer changes in the auto industry through continuous investment in R&D and advanced dealer network programs. Highly recognized for its sharp sales increase, first-rate dealership programs, and growth in brand awareness, Hyundai Motor Company beat other candidates including Ford, Jaguar, and Landrover to be selected as the winner of the coveted title. In 2008, UK’s Autocar selected Hyundai Motor Company as Automaker of the Year, praising Hyundai for having “grown into a top-class global automaker with its competitive products.”
Effect of Political and Legal Environment
The increase in the relationship between the different countries and their government is a good indicator for the business of Hyundai as it operates its business in various countries. It would generate business expansion opportunity for Hyundai. In order to ensure the proper compliance of the business activities with the applicable legislation, the corporation works on certain guidelines for the different business operation in different countries. It is essential as every country has different rules and business regulations.
Effect of Socio-cultural environment
The socio-cultural factors also affect the business effectiveness and performance. The business of Hyundai is operated in the several countries worldwide and the society and culture of those countries are entirely different (Wessels, 2000). The management of the company operates its business by studying the social and cultural factors of the country effectively.
Effect of Ethical Environment
Hyundai Corp. introduced Ethics Management at the beginning of year 2004, to build the basis for survival on its own and to seek mutual benefit of all parties involved including customers and business partners etc. by preventing moral hazard of the employees and implementing transparent, responsible, and honest management.
The company organized its Ethics Management Office, with the Executive Director of the Corporate Planning & Personnel Management Office serving as the Chief Ethics Officer, and also established the Principles of Business Conduct, the Code of Conduct, and the Self-Review Questionnaire.
The Questionnaire pops up from the initial windows screen every day during the first week of any month when the employees check in to the intranet system, to remind them of and draw their voluntary participation to the idea and pursuit of Ethics Management in practice.
Special training and educational sessions on best practices of ethical management from leading corporations and institutions will be presented regularly to the staff.
All the members of the company have submitted his or her own pledge of compliance to the various ethics codes, and those in violation will be subject to discipline by the Human Resources Committee following due examination by the Ethics Management Office.
Effect of Technological Environment
The management of the company is continuously involved in using world class technology in order to achieve technological advancement. The use of most modern technologies causes an increase in customer service effectiveness.
Financial data
The business strategies of Hyundai are to increase the opportunities through the environmental factors is effective as it is causing an increase in the number of sales units continuously. But in the last year the economic factors has affected the sales of the business as total number of units sold were 1668745 in the year 2008, which is less in comparison of the year 2007 in which it was 1700297 units (Hyundai Motor Company, 2010). The decrease in the sales was domestically due to fluctuation in the current rate as well as in commodity rate.
Recommendation
There are various alternative strategies, which can be adopted by the management of Hyundai in order to improve business performance such as integration strategy, growth strategy etc. The company should use the integration strategy to expand the business worldwide. It would be beneficial for the business as it would reduce the impact of political and legal factors on the business operations. The affect of the economic factors would also be less due to proper knowledge of the customer behavior, their buying pattern in an effective manner.
Implementation of Strategy
Hyundai could implement the integration strategy in an effective manner through its diverse workforce and business activities. The diverse workforce would be beneficial to develop the motivation techniques within the organization according to their culture and beliefs (Ryall & Craig, 2003). For the effective implementation of the integration strategy the management of the company should develop a proper plan related to the various aspects of the business operations.
Evaluation & Control
Implementation of the integration strategy is not sufficient itself for the business effectiveness. The evaluation of the business effectiveness in timely manner is essential for rapid growth of the business. Company administration should periodically review its implementation process which is necessary for its efficient applications and future results (Ryall & Craig, 2003). This step makes implementation process effective.
-
Digital marketing campaign
Digital marketing campaigns can help you get more traffic, improve your brand awareness, drive more sales, and much more.
But, executing a digital marketing campaign can seem like a complex process. After all, there are dozens of different platforms, and hundreds of different strategies you can execute.
But, by taking the time to plan out your digital campaign step-by-step you can increase your chances of success while reducing overwhelm across the board.
In this post, you’ll learn what a digital marketing campaign is, and a 10-step process you can follow to execute and build a digital marketing campaign.
What is a digital marketing campaign?
A digital marketing campaign is a strategic online marketing effort that’s executed to achieve a specific goal. Usually, the end result will lead to greater brand awareness, more traffic, improved conversions, or more revenue.
The purpose of planning out a digital campaign is to help you articulate who your audience is, what goal you want to achieve, and the process you’re going to take to achieve that goal.
Putting together a successful online marketing campaign can be a lot of work, and there are a lot of moving pieces you’ll need to get right.
How to start an online marketing campaign
These are the 10 steps for building a successful digital marketing campaign.
- Set your marketing goals
- Identify your target market
- Carry out a keyword and topic research
- Do market research and competitor analysis
- Choose your delivery channels and set your budgets
- Create your content assets
- Run pilot campaigns first
- Monitor the campaigns and analyze their performance
- Allocate more budget to profitable activities
- Set up remarketing campaigns
Step 1: Set your marketing goals
The first thing you need to do is figure out why you’re running a digital marketing campaign in the first place.
The options are nearly endless, but if you try and pursue too many goals at once you’re not going to achieve any of them. For example, do you want to improve your conversions, grow your email list, improve your traffic, rank for more keywords, get more followers?
There are a handful of different types of goals, brand awareness, increase in sales, lead generation, and social follower growth. Some of these goal types are easier to quantify than others.Example of Digital Marketing Goals (source: CMI)
For example, it’s much easier to see if your email list has new subscribers than to see if more people are aware of your brand. However, you’ll want to try to ground these goals with data as much as possible.
Here are some examples of attainable goals:
- Improve brand awareness by getting 5 mentions from major news outlets/websites
- Increase search engine traffic by 5,000 visitors per month in 45-days
- Double social media followers to 10k by the end of 2020
- Improve sales by 200% by adding an abandoned cart sequence to our eCommerce store
- Add 500 new qualified email subscribers in 30 days
Each goal you set will have a plan of action. For instance, if your goal is to increase organic traffic, then this will include evaluating your existing content, doing keyword research, updating older content, writing new posts, and even doing backlink outreach and promoting your content across social media.
You can run as many online marketing campaigns as you want. Overall, you’ll want to create a specific measurable outcome for every campaign you run.
This allows you to dig into your data to see what’s working, so you can refine your digital marketing strategy moving forward.
Step 2: Identify your target market
Do you know your audience? Before you start a marketing campaign you’ll need to define the exact audience you’re going to target.
If you don’t know this exact person yet, then you’ll need to spend some time thinking about and researching who this person is.How to Define Your Target Market
One of the best ways to do this is to create what’s called a buyer or customer persona. This is a description of your ideal customer, and will include information like:
- What they do for a living
- How much money do they earn
- What their family situation is like
- Their age
- Any hobbies they have
When creating an ideal customer persona you should also include:
- What other types of websites do they visit online
- The goals they have when visiting your site
- Any fears or desires they have
If you’ve never done this exercise before, you can actually pull information about your target market from existing data.
One of the best sources of this will be Google Analytics. If your website has been getting traffic, then you can pour through your data to pull out information like:
- Age
- Gender
- Where they’re from
- How they navigate your website
- The types of content they value the most
All of this should be combined into a document or user profile, you can even include images, so anyone working on the campaign can visualize this person.
If you have multiple different audience segments, then you’ll want to do this process multiple times and create customer avatars for each segment of your audience or market you’re targeting.
Step 3. Carry out a keyword and topic research
By now you should have a clear idea of your ideal result and you’ll have a detailed view of the type of people you want to target.
By uncovering the right keywords you’ll know exactly what potential readers and customers are typing into Google to answer their questions, or find the products and services you offer.Topic Research using SEMRUSH
Regardless of the channel, you should do keyword research to uncover topics and keywords that your readers want to hear about.
No matter if you’re creating an SEO, PPC, email, Facebook, or an entirely different campaign, keyword research can help to move you in the right direction.
The goal of keyword research is to put yourself in your customer’s shoes and think about the kinds of keywords they’ll be typing into Google (or another platform) when searching for your products and services.
Spend time brainstorming keywords that fit this description and then run these keywords through keyword tools to find SEO keywords and phrases that have decent volume and not much competition.
Other ways to brainstorm keywords:
- Search for your market on Quora to find questions related to your niche
- Use a tool like Answer the Public to find question-based keywords
- Use Google Keyword Planner to find out the exact search terms types by users on Google search.
Once you have your initial list you can use these seed keywords and run them through a tool like SEMRush for detailed keyword analysis.
PPC keyword research
If you’re going to be running a paid advertising campaign your keyword search will be a little different. You’ll also have to compare the cost per click of each keyword and group these keywords into different groups.PPC Keyword Research
When you run PPC ads you pay whenever a visitor clicks on your ad and visits your website. So, your goal is to keep your cost per click (CPC) low, while still reaching a solid volume of people.
Once you’ve found the keywords you want to target for your PPC ads, you’ll use these to help create your ads. For example, you can include your target keywords in your headline and body copy.
Step 4: Do market research and competitor analysis
With an understanding of your customer, you’ll also need to figure out where they hang out online and what your competitors are doing.
This will help you better plan a campaign and give yourself the best chance of your campaign succeeding.
You can also model your campaigns off of what has been successful for your competitors. This allows you to shortcut the process and give yourself a greater chance of your campaign succeeding.
Here are a few questions to ask when researching your competitors:
- What kind of products are they promoting/what’s selling well?
- What kind of content is working well for my competitors?
- What popular products and services are being sold in my market?
You can also use tools like Buzzsumo, and even a simple Google search to find content that’s incredibly popular in your space. It can be helpful to study content that’s been incredibly popular since it’s tapping a deep need in your niche and successfully speaking to a large portion of your market.
If you’re going to be running a Facebook ad campaign there’s a tool you can use called Facebook Library Ads which allows you to search through ads related to your niche that have been successful in the past.Use the Facebook Ads Library to Learn More About Your Competitor’s Tactics
Step 5: Choose your delivery channels and set your budgets
As you start to execute digital marketing campaigns you’ll probably create campaigns across a wide range of digital channels. However, when you’re first starting you’ll want to focus on only one or two channels.
For example, you have Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Pinterest in the social media space. You have Google ads, content marketing, onsite and offsite SEO, email marketing, and a lot more.
Chances are you’re going to be using a combination of different channels. But, you’ll have one main channel that ties into your goal.
If your goal is to increase your email subscribers by 500 in 30 days there are all kinds of tactics you can employ the achieve that goal:
- Test different email opt-in form copy and placement, including pop-ups
- Optimize your existing content and create new content focused on pushing people to your list
- Create value-add email newsletters that encourage readers to forward to a friend
- Guest blog on popular sites in your niche with links back to an opt-in page
- Share the link to an email subscriber page on your social media profiles
As you can see there are a lot of different overlapping channels you can utilize to help you achieve your main goal of growing your email list.
Before you start creating your campaigns you’ll want to define the channels you’re going to utilize.Digital Marketing Channels
For any digital marketing campaign you’re running you need to come up with a budget. Digital advertising is the cheapest form of advertising, but you’ll still need to set aside a budget.
Even running organic campaigns will require an investment of time or money. For example, you can do keyword research, write your content, and do backlink outreach yourself, or you can pay someone else to do it for you.
Other forms of digital advertising will cost right from the start, like paid advertising.
Your budget needs to take into account anything you’ll be spending within your company, plus costs to any external companies or contractors you’ll be using to create creative materials, or even manage your campaigns for you.
Step 6. Create your content assets
Depending on the campaign you’re running, there are different content assets you’ll need to create.Content Types
Here are a few examples:
- If your goal is to grow your organic search engine traffic, then you’ll have to create a series of blog posts.
- If you’re going to be running Facebook or Instagram ads, then you’ll need to create all of your ad creative materials and landing pages you’ll be sending traffic to
- If you’re executing a video marketing campaign, then you’ll need to create, edit, and publish a series of videos
All of the previous steps will help you create content assets that will serve the campaign goal you decided on early on.
Some content assets, like blog posts, and videos will be relatively static once you create them. However, you’ll be more creative with how you choose to promote and will refine your strategy based on which promotion tactics get you closer to your goal.
However, if you’re running a digital advertising campaign, your content assets will evolve based on the data. Maybe you’ve found that a certain type of image performs better than the rest, or that a certain headline results in 10% more sign-ups. Your audience targeting will stay relatively the same (targeting your ideal customer), while your ad creative will evolve based upon what your market responds to most.
Step 7. Run pilot campaigns first
If you’re running advertising campaigns or any kind of paid media campaigns, you’ll want to run test campaigns first, so you don’t blow through your entire budget.
With your test campaigns, you’ll start with a small budget and make refinements as you get feedback and data. For example, when you’re creating ads you could test different headlines, different images, body copy, CTAs, and more.
You’ll want to strike a balance between keeping your initial budget small, while still getting enough data to refine your ads.
If you’re doing paid advertising, even something as small as $1-10 per day will give you enough data to work with if you let it run for a month.
If you’re paying for content it’ll be more difficult to see instant feedback, however, you can see how your audience reacts to your articles via the comments section, social shares, sign-ups, and clicks (if you’re promoting your blog posts to your email list
Step 8: Monitor the campaigns and analyze their performance
With digital marketing campaigns, there’s no shortage of data available. Whatever platform you’re utilizing, you’ll be able to find all kinds of data.
For example, email marketing tools have built-in analytics, every advertising platform has its own ad dashboard, and there are a variety of third-party tools you can use for website statistics, and more.
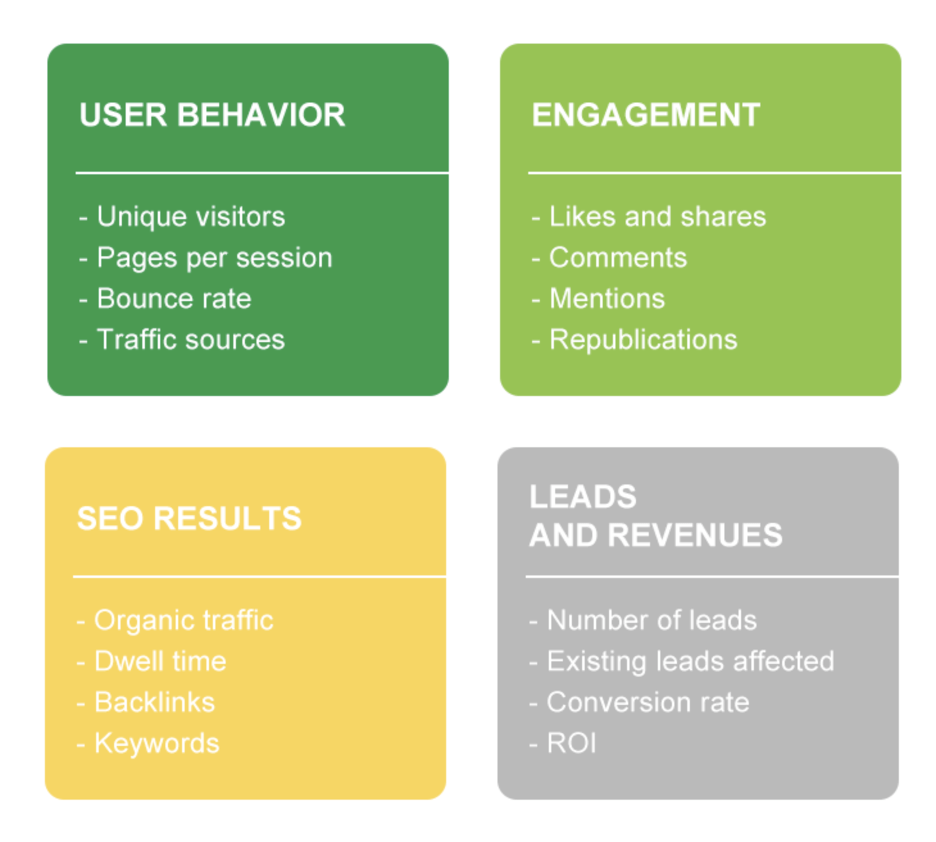
Digital Marketing KPIs However, before you start pouring over data you’ll want to refer back to your goals. This will help you zero in on the numbers that actually matter. Once you can analyze those numbers you can figure out what’s working and what isn’t, so you’ll have insights you can take action on.
Step 9: Allocate more budget to profitable activities
Once you’ve been able to see which campaigns are generating the most results, it’s time to double down. By now you know that you won’t be wasting your money on certain activities, and they’ll be able to generate a verifiable return.
However, you’ll still want to scale your investment up slowly instead of spending all of your remaining budgets right away. It can be tempting to invest everything, but as you start to allocate more of a budget you’ll still continue to get data.
Then, you can use that data to further refine your campaigns. Eventually, you’ll reach a point where your campaigns are about as optimized as possible. When you reach this point and you’re getting the highest ROI and conversion rates possible, then it’s really time to scale up.
Step 10: Set up remarketing campaigns
Remarketing is something you should be using throughout your entire campaign, especially if you’re using digital advertising.
Remarketing is the process of running ads to visitors who have already visited your website. These ads will appear wherever else your visitor is online including, watching YouTube videos, reading a blog, scrolling through social media, or browsing the web.
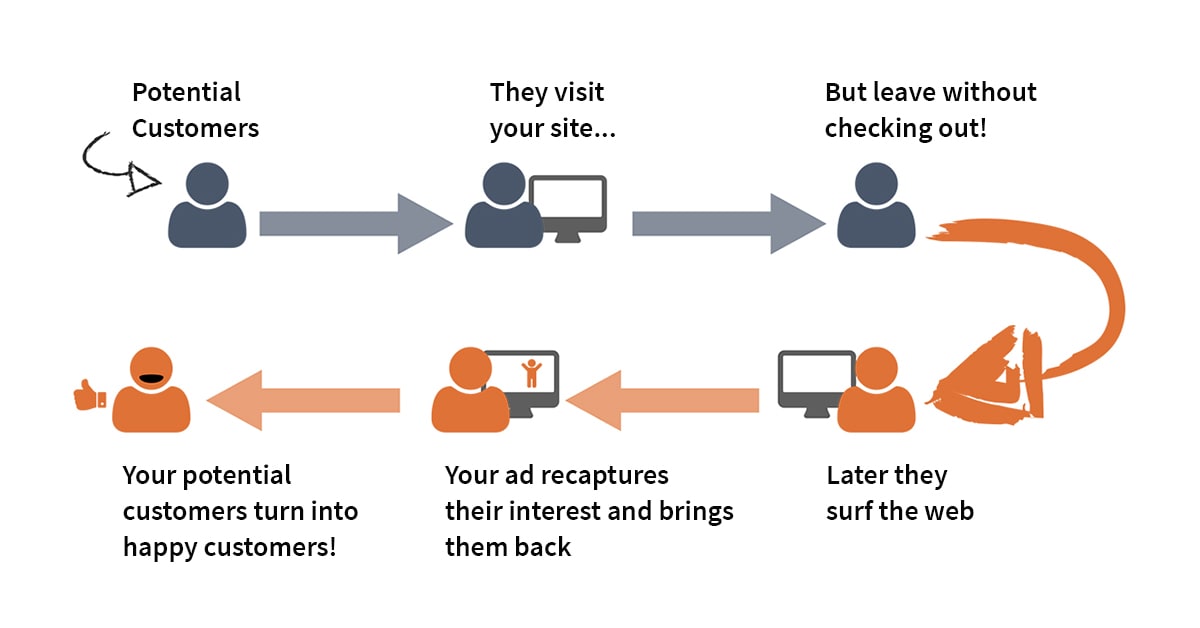
How Retargeting Works This allows you to generate more sales than you otherwise would have missed out on. If someone is looking at one of your products, or visits a certain page on your site, but doesn’t make a purchase, you can target this person with a variety of ads. The most common are Facebook ads and Google ads.
These ads will essentially follow this person around the web and direct them back to your website to complete their purchase. You can even add a coupon to these ads to make your visitor’s purchasing decision much easier.
Remarketing ads are available across every big digital advertising platform including, Facebook ads, and Google ads.
Another form of remarketing that doesn’t rely on advertising is email marketing. You can create a cart abandonment email sequence that will automatically get sent out to your visitors if they add items to their cart, but don’t complete the purchase.
People are incredibly busy and distracted these days, so there are a number of reasons that they’d forget to complete their purchase. A cart abandon sequence can be a single email reminder or an entire series of emails that get sent out at a certain interval.
Adding remarketing campaigns to whatever campaign you’re running will help to plug any conversion holes and make sure that you’re getting the most out of the new traffic you’re generating for your website.
-
startup scenarios in india
a startup is a newly formed business with particular momentum behind it based on perceving demand for its product or service.the intention of startup is to grow rapidly as a result of offering somethimg that adresses a particular market gap.
Top startups in india
BOAT,NYKAA,UDAAN,SWIGGY,POSTMAN,SLICE,ATHER .these are some of the strartups that are booming in india.
Growth of startups in india
startups in india have grown remarkable over the last six years.the number of new recoginised startups has increased to over 14,000 in 2021-22 from only 733 in 2016-17 the survey said. india has become the third largest startup ecosystem in the world after us and china
Reasons why startups fail in india
India is third largest ecosystem for startups, yet 80%-90% of india startups fail within the first 5years of their inception.here are some key reasons startups fail in india.
LACK OF INNOVATION : according to survey,77% of venture capitalists think that indian startups lack innovation or unique business models.
LACK OF FUNDS: in 2008, the rental startup, TAZZO,shut shop, the reason, as given by one of its funding partners, was a failled product-market fit that led to drying up of funding. there are millions of startup ideas floating around. but to turn ideas into reality requires finance. lack of funding is one of the key reasons why startups fail.
LACK OF FOCUS:when bill gates and warren buffeet were asked about one factor that was responsiable for their success, both repiled with one word.”FOCUS” to understand focus we need to go for example grubhub is a food delivery startup.from the beginning, the company decided to focus only on food delivary. there’s a lot of other services that a company like taht could offer-pick up of food, catering,and more, but the founders chose to focus on jsut delivery. the result? they could execute technically and operationally and grow the business successfully.by look in feedback, both good and bad.do not go all out. decide and focus on one thing at a time.
UNICORN IN STARTUPS
The term unicorn refers to any startup that reaches the valuation of $1 billion. the term was first coined by AILEEN LEE, founder of cowboy venture when she referred to the 39 statups that had a valuation of $1 billion as unicorn. there are 105 unicorns in india the total valuation is $338.50 Bn. the year 2021, 2020, and 2019 saw the birth of the maximum number of unicorns in india. the first unicorn was seen in india in 2011, examples of unicorns in india are. zomato , phonepe , byju’s and soo on..
FEATURES OF STARTUP
HIGH GROWTH: startups exist to grow. if you start a plumbing business, just making enough profit to support your lifestyle may be enough, but a startup aims much higher some people say a startup should be growing 5-7% a week. of course, that’s just an estimate, and actual growth rates vary widely.
DOING THINGS DIFFERENTLY
To achieve that high growth, startups usually do things differently. that doesn’t necessarily mean inventing a whole new industry, but its means taking a markedly different approach to the companies that are already established.
COMMITMENT
Starting a business- any kind of business- can be a huge and all- consuming endeavour. most people who do it are very committed, and end up working long hours and putting their heart and soul into making it work.
STRONG INCENTIVES
Startup employees aren’t only committed because of idealism. stock options also help. in fact, when startups are hiring new employees, particularly in the very early stages when they don’t have much funding, they may not be able to offer very high salaries. what they offer instead is the chance to take a real, monetary stake in the future of the company, potentially enjoying a huge windfall if it takes off.
-
Bandipura tiger reserve and national park

Bandipur National Park is a national park covering 868.63 km2 (335.38 sq mi) in Chamarajnagar district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It was established as a tiger reserve under Project Tiger in 1973. It is part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve since 1986.The Maharaja of the Kingdom of Mysore created a sanctuary of 90 km2 (35 sq mi) in 1931 and named it the Venugopala Wildlife Park. The Bandipur Tiger Reserve was established under Project Tiger in 1973 by adding nearly 800 km2 (310 sq mi) to the Venugopala Wildlife park.Bandipur National Park is located between 75° 12’ 17″ E to 76° 51’ 32″ E and 11° 35’ 34″ N to 11° 57’ 02″ N where the Deccan Plateau meets the Western Ghats, and the altitude of the park ranges from 680 meters (2,230 ft) to 1,454 meters (4,770 ft). As a result, the park has a variety of biomes including dry deciduous forests, moist deciduous forests and shrublands. The wide range of habitats help support a diverse range of organisms. The park is flanked by the Kabini river in the north and the Moyar river in the south. The Nugu river runs through the park. The highest point in the park is on a hill called Himavad Gopalaswamy Betta, where there is a Hindu temple at the summit. Bandipur has typical tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The dry and hot period usually begins in early March and can last till the arrival of the monsoon rains in June.
Flora:
Bandipur supports a wide range of timber trees including: teak (Tectona grandis), rosewood (Dalbergia latifolia), sandalwood (Santalum album V), Indian-laurel (Terminalia tomentosa), Indian kino tree (Pterocarpus marsupium), giant clumping bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus), clumping bamboo (Bambusa arundinacea) and Grewia tiliaefolia.
There are also several notable flowering and fruiting trees and shrubs including: kadam tree (Adina cordifolia), Indian gooseberry (Emblica officinalis), crape-myrtle (Lagerstroemia lanceolata), axlewood (Anogeissus latifolia), black myrobalan (Terminalia chebula), Schleichera trijuga, Odina wodiar, flame of the forest (Butea monosperma), golden shower tree (Cassia fistula), satinwood (Chloroxylon swietenia), black cutch (Acacia catechu), Shorea talura (E), indigoberry (Randia uliginosa).
Fauna:Bandipur National Park harbours Indian elephant, gaur, Bengal tiger, sloth bear, mugger crocodile, Indian rock python, four-horned antelope, golden jackal and dhole.The commonly seen mammals along the public access roads in the park include chital, gray langur, Indian giant squirrel and Indian elephant. A list of medium to large-sized mammals in the park is given in the following census table published in 1997
Birds:Peafowl are among the most commonly seen birds in Bandipur along with grey junglefowl, crows and drongos. Bandipur is home to over 200 species of birds including honey buzzards, red-headed vultures, Indian vultures, flowerpeckers, hoopoes, Indian rollers, brown fish owls, crested serpent eagles, changeable hawk-eagles, bee-eaters and many kingfishers and ospreyss are a common sight in winter.
Best time to visit:Best period to visit this place in monsoon season is between July and September. Summers in this part of the country usually remain normal and less warm hence the temperature fluctuations vary in range from 32°C-38°C. Best period to visit this place during summer is from March-May
Famous for:Bandipur National Park second highest Tiger population in India. Bandipur National Park is located in Gundulpet taluk, Chamarajanagar district. Park is the part of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve making it largest protected area in Southern India and largest habitant of Wild Elephants in South Asia.
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.